Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids
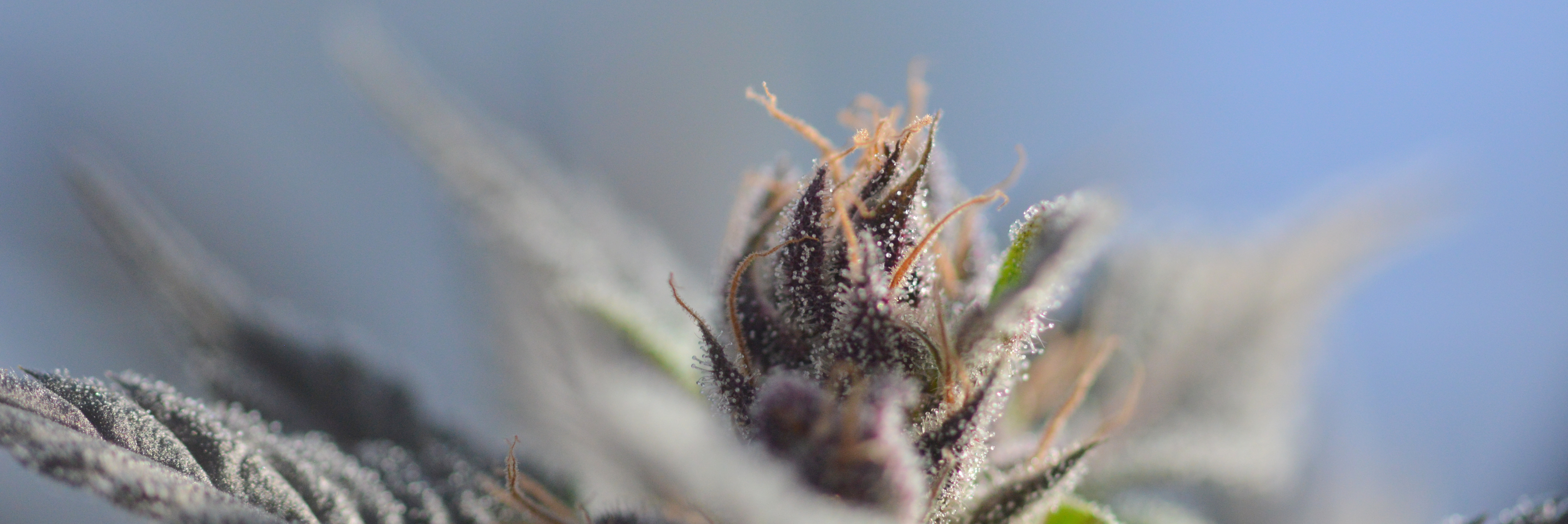
Cannabinoids are a class of diverse chemical compounds that act on cannabinoid receptors in the body.
Phytocannabinoids are a class of molecules in the cannabis plant, contrary to endocannabinoids are produced in the human body or mammal.
The plant contains more than 100 cannabinoids, The most active are: THC, CBD, CBN, CBG
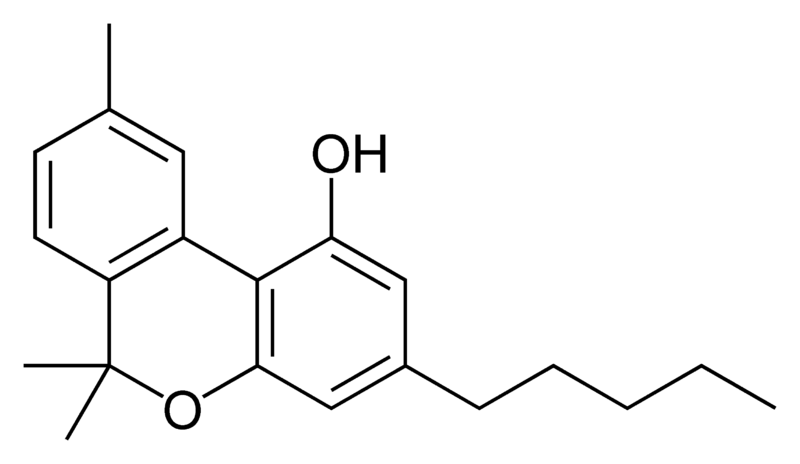
Cannabinoids impact cannabinoid receptors in the body. Today, two main receptors are known, CB1 and CB2. CB1 is present mostly in the nervous system, and CB2 in the periphery, especially in the immune system and digestive system. THC binds to both of these receptors in the body. CB1 is responsible for THC’s neural properties – relaxation, pain relief (though CB2, scattered in the peripheral nerves, also contributes to pain relief), tremors, spasms, and in higher doses on psychotropic symptoms and euphoria. CB2 is responsible for the anti-inflammatory properties of cannabinoids. CBD, the main non-psychotropic cannabinoid, is active primarily on the anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidizing mechanisms.
CBN
C
CBG
CBC